
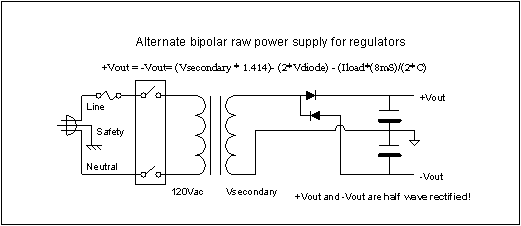
- #Design of simple dc power supply using bipolar transistor full
- #Design of simple dc power supply using bipolar transistor series
#Design of simple dc power supply using bipolar transistor series
In this way, the current is reduced the greater the overload, and thereby the risk of damage is reduced.įoldback current limiting in a voltage regulator reduces the power consumption, because as the overload increases, so the current folds back and the overall power consumption falls, keeping the series pass transistor heat dissipation within more reasonable bounds. At this point, rather than just limiting the current, the current actually starts to reduce.

In this type of current limiting used in regulated power supplies, the output voltage is maintained until the point where the current limiting starts to come into action. This is not ideal because at the electronic circuit design stage, allowance needs to be made for this, requiring, possibly a larger series pass transistor as well as additional heat sink capability, adding additional cost and size to the regulated power supply.
#Design of simple dc power supply using bipolar transistor full
This increases the power dissipation within the device.Īt the point where the output voltage is nearly zero, the maximum current is drawn whilst the voltage across it, is that of the full input voltage from the smoothing and rectifier circuits.

One of the disadvantages is that as the current limiting starts to operate, the maximum current is drawn, but at this point the output voltage falls, meaning that the series pass transistor in the regulated power supply has an increased voltage across it. The circuitry is simple and uses just a few electronic components but it does not reduce the current in the case of a short circuit - it is maintained at the maximum level and this could give rise to damage within the circuitry. This is the most basic form of current limiting used in regulated power supplies. At this point the current maintained at this level whilst the voltage falls with increasing load. Using constant current limiting, the output voltage is maintained as the current rises until a point is reached where a maximum is reached. There are two main types of current limiter circuit: The same is true of the current limiters using within regulated power supplies where the current limiter circuits fall into particular categories. Types of current limitingĪs with any technology and type of electronic circuit, there are a few options from which to choose and choices need to be made dependent upon the particular requirements for the electronic circuit design. These circuits are more applicable to linear power supplies, although similar sensing techniques can be used in switch mode power supplies. In view of the possible damage to a power supply in cases of overload, current limiters are almost always fitted, and they are a standard feature incorporated into regulated power supply ICs.Īs the name suggests, the current limiting circuit limits the current from the regulated power supply to a maximum amount determined by the circuit, and in this way, severe damage to the circuits, both the power supply and the circuit being powered can be avoided.
See also: Power supply electronics overview Switch mode power supply Capacitor smoothing Over-voltage protection PSU specs Digital Power Power management bus: PMbus Uninterruptible power supplyĬurrent limiter circuits are key to power supplies, protecting them in cases of a short circuit or other overload condition. Linear power supply Shunt regulator Series regulator Current limiter 78** series regulators & circuits LM317 voltage regulator & circuits LDO, low dropout regulators

Linear Power Supply Circuits Primer & Tutorial Includes: Power Supply Current Limiter Circuits Current limiter techniques and circuits using diodes and transistors to provide a current limiter function for power supplies and other circuits.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
